The recent developments in quantum computing have opened up new possibilities for algorithmic speedup, as demonstrated in a paper published in Science Advances. The study, conducted by researchers at JPMorgan Chase, Argonne National Laboratory, and Quantinuum, highlights the potential of the quantum approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA) in various industries such as logistics, telecommunications, financial modeling, and materials science.
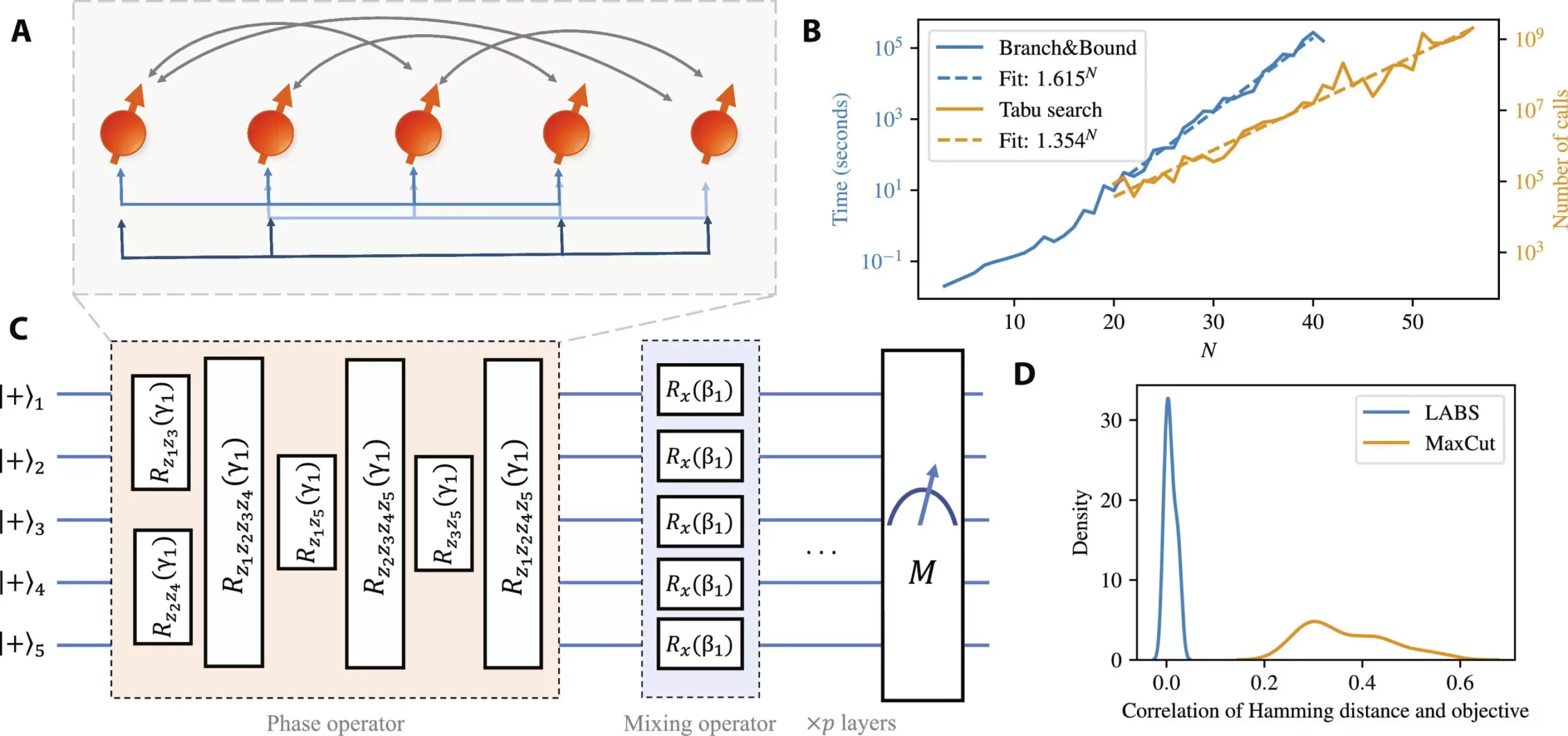
The researchers sought to determine if a quantum algorithm like QAOA could outperform classical methods in solving complex problems. By applying QAOA to the Low Autocorrelation Binary Sequences problem, the study revealed that the quantum algorithm’s efficiency improved significantly as the problem size increased. This indicates a potential quantum speedup compared to classical solvers, paving the way for future advancements in quantum computing.
To assess the quantum algorithm’s performance in an ideal noiseless environment, JPMorgan Chase and Argonne collaborated to develop a simulator using the DOE petascale supercomputer Polaris. This simulation allowed for the evaluation of the algorithm at scale, showcasing the potential of high-performance computing in advancing quantum information science. The results highlighted the efficiency of large-scale quantum circuit simulations in enhancing quantum algorithmic performance.
Taking a step towards practical application, the researchers implemented a small-scale version of the algorithm on Quantinuum’s System Model H1 and H2 trapped-ion quantum computers. Through algorithm-specific error detection techniques, the team successfully reduced the impact of errors on algorithmic performance by up to 65%. This demonstrates the feasibility of integrating quantum algorithms with error-correction mechanisms on current quantum computing platforms.
The collaborative efforts between JPMorgan Chase, Argonne, and Quantinuum have resulted in a significant milestone in quantum computing research. By leveraging the unique capabilities of Quantinuum’s H-Series Quantum Computer, the research team was able to achieve groundbreaking results in algorithmic speedup. This partnership underscores the importance of collaboration in driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of quantum computing technology.
Overall, the study signifies a promising future for quantum algorithms in revolutionizing various industries and unlocking new possibilities in solving complex problems. The implications of quantum algorithmic speedup extend beyond theoretical research, offering practical solutions for real-world applications in fields ranging from finance to cryptography. As the field of quantum computing continues to evolve, it is crucial for researchers and industry partners to collaborate on advancing quantum algorithms for the benefit of society as a whole.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.