The idea of luminescent solar concentrators (LSC) has been around since the 1970s, with the goal of improving solar energy capture by using luminescent materials to concentrate sunlight onto photovoltaic (PV) cells. Traditional concentrators rely on mirrors and lenses, but LSCs have the unique ability to harvest diffuse light, making them ideal for applications like building-integrated photovoltaics. However, scaling up LSCs to cover large areas has been a challenge due to issues like self-absorption within the waveguide. Researchers at Ritsumeikan University in Japan have introduced an innovative “leaf LSC” model to address these limitations and enhance light collection and transfer to PV cells.
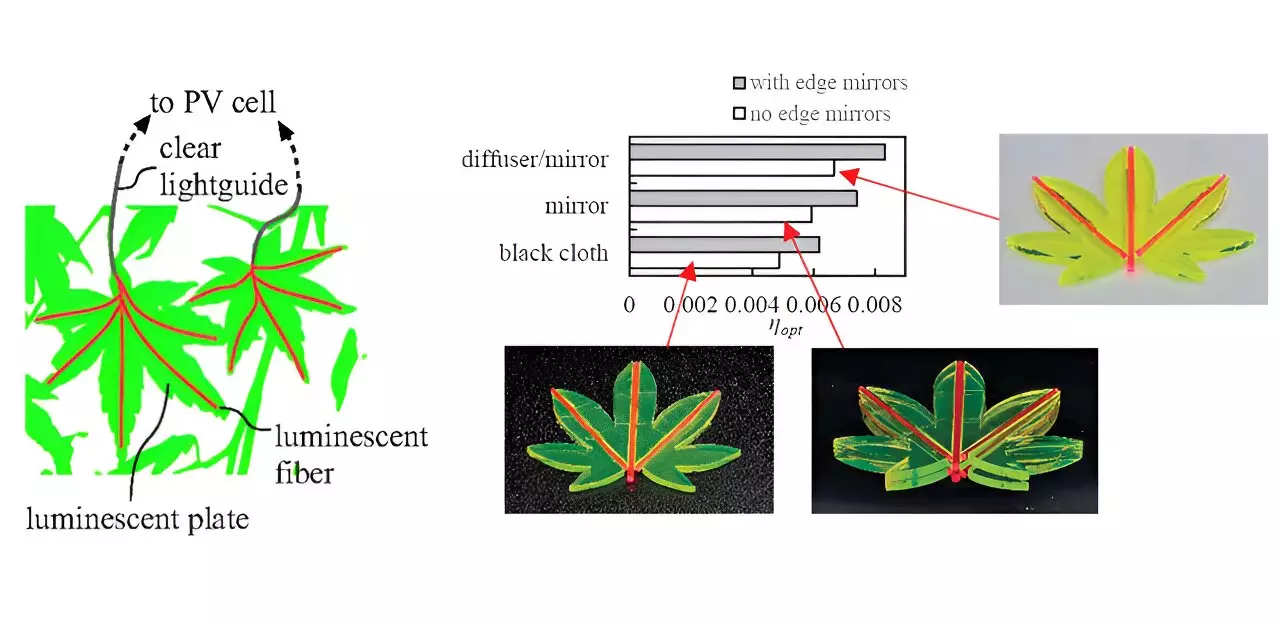
The leaf LSC design tackles the scalability issue by utilizing smaller luminescent components arranged like leaves on a tree. Luminescent plates surround a central luminescent fiber, with the plates’ sides facing the fiber. This setup allows incident photons to be converted into photoluminescent (PL) photons by the plates, which then travel through the fiber and are collected at its tip by a PV cell. Clear lightguides connect multiple fibers to a single PV cell, increasing the incident area of the LSC and reducing photon losses due to self-absorption and scattering.
The modular approach of the leaf LSC design offers several advantages. By reducing the lateral size of individual modules, researchers have found that the efficiency of photon collection improves significantly. For example, decreasing the side length of a square leaf LSC from 50 mm to 10 mm resulted in a notable increase in photon collection efficiency. Additionally, the modular design allows for easy replacement of damaged units and integration of advanced luminescent materials as they become available.
Researchers have enhanced the efficiency of the leaf LSC design by incorporating techniques from traditional planar LSCs, such as edge mirrors and tandem structures. Through experiments, they were able to calculate the optical efficiency of these leaf-like structures analytically based on the spectrum and intensity of incident light, using a single-spot excitation technique. This integration of proven techniques into the innovative leaf LSC design showcases a creative approach that boosts the efficiency of solar concentrators.
Optimizing photon collection in LSCs through the leaf LSC design may pave the way for more flexible and scalable solar energy solutions. This approach to energy harvesting has the potential to revolutionize the application of solar concentrators, making them more efficient and adaptable for various uses, from large-scale installations to building-integrated systems. As technology continues to advance, the promise of significantly enhancing the performance of solar energy systems and contributing to more sustainable energy solutions becomes more tangible.
The development and implementation of leaf LSC technology mark a significant step forward in the field of solar energy capture. By combining innovative design with traditional techniques, researchers have created a solution that holds the potential to reshape the way we harness solar power. The future looks bright for solar energy solutions, with leaf LSC technology leading the charge towards a more sustainable and efficient energy landscape.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.