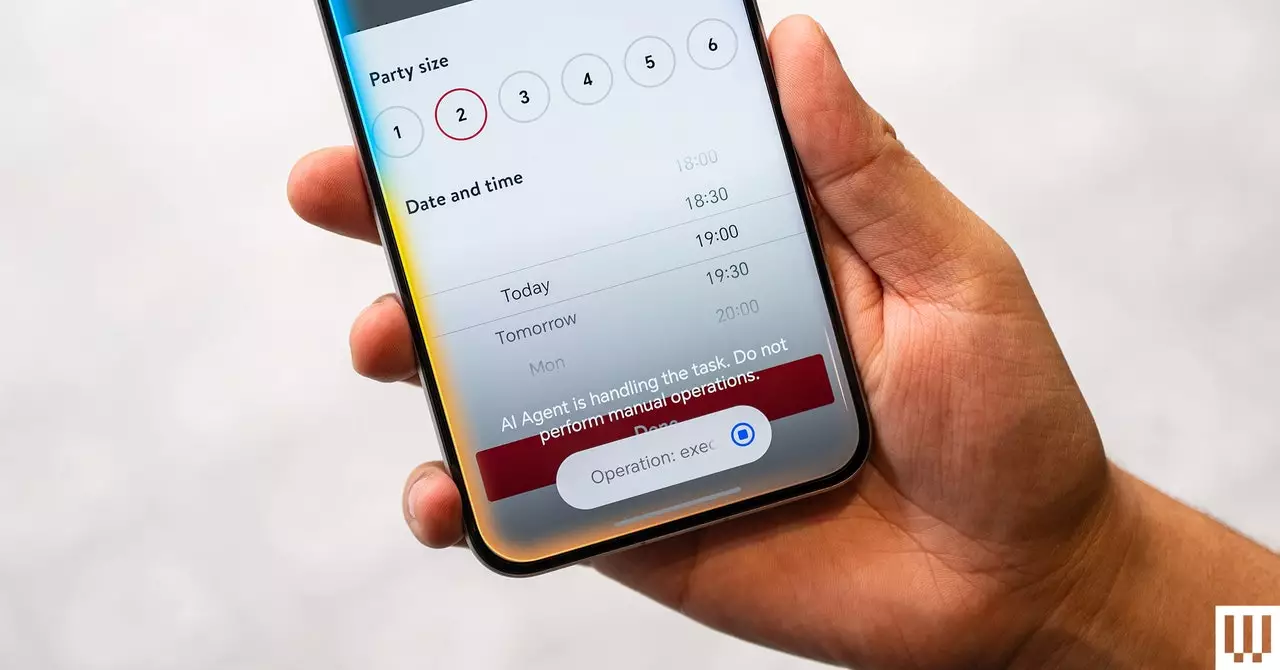
In the ever-evolving world of technology, the integration of artificial intelligence in everyday tasks presents both remarkable conveniences and notable challenges. One emerging scenario involves using AI to book restaurant reservations. While this advancement seems promising, it also leads to complications, as highlighted in a recent example where an AI assistant selected a restaurant but faltered at the reservation stage due to a credit card requirement. This situation underscores a fundamental limitation: despite advancements, AI still requires human intervention to finalize transactions. The inability to complete bookings without direct human input raises questions about reliability and user experience.
Another noteworthy aspect observed in AI functionality is the flexibility in user queries. For instance, when prompted to find a “highly rated” eatery, the AI effectively filters options based on review scores. However, the assistant’s methodology does not extend beyond this basic evaluation, lacking the capability to cross-reference data from multiple sources or platforms. Such mechanics indicate a disparity in how these systems analyze information, relying solely on internally processed data, which can limit their effectiveness. This raises the concern that while these AI models can provide quick suggestions, they may not always guarantee the best choices for consumers, leaving room for improvement in data integration.
AI Evolution and the User Experience
Recently, tech innovations have focused on agentic AI—a trend that embodies the potential for AI systems to execute tasks independently. For example, Google’s Gemini 2 AI model offers a glimpse into a future where AI engages proactively, acting on users’ behalf. This approach, along with explorations at events like MWC 2024, indicates a shift toward generative user interfaces. The idea is revolutionary: instead of users navigating traditional apps, they command AI assistants to create a bespoke interface tailored to their requests. This could streamline interactions significantly, enhancing ease of access to services.
One intriguing comparison arises when examining Honor’s method of training its assistant, reminiscent of Rabbit’s Teach Mode. In this model, users proactively guide the AI on completing tasks, eschewing the conventional reliance on APIs for cross-application communication. This shift highlights a manual process of teaching that emphasizes user control. While such an approach empowers users to define how they want their tasks executed, it begs the question of how scalable and efficient this manual training can be as the number of tasks expands.
The journey of integrating AI into daily tasks such as restaurant bookings illustrates the balance between innovation and practicality. While there is significant excitement around agentic AI and its capabilities, the integration process still necessitates human involvement and strategic oversight. Future iterations of these technologies need to focus not only on autonomy and flexibility but also on seamless integration with existing data, enhancing user experience while reducing friction in everyday tasks. The potential for AI to redefine how we interact with services is immense, but it must evolve thoughtfully to meet user needs effectively.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.