Metal halide perovskites have emerged as a promising material for the development of thin-film transistors with exceptional optoelectronic properties. While tin halide perovskites have demonstrated impressive field-effect mobilities in p-type transistors, the challenge lies in achieving similar performances in n-type transistors to enable the development of complementary logic circuits.
Researchers have observed that perovskite channels based on tin are not well-suited for the fabrication of n-type transistors, limiting the potential for complementary logic circuits. As a result, there has been a recent exploration of other metal halide perovskites, such as lead halide perovskites, for designing n-type thin-film transistors.
Lead halide perovskites have shown promise for n-type transistor applications, but their ionic defects have confined electron mobilities to lower values. To address this issue, researchers at various institutes globally have introduced a novel strategy using formamidinium lead iodide (FAPbI3) perovskite to fabricate n-type transistors with significantly improved field-effect mobilities.
By incorporating a methylammonium chloride (MACI) additive, the research team was able to enhance the performance of their n-type transistors. This additive not only regulated strain in the perovskite but also improved its overall properties, leading to more stable and efficient transistors.
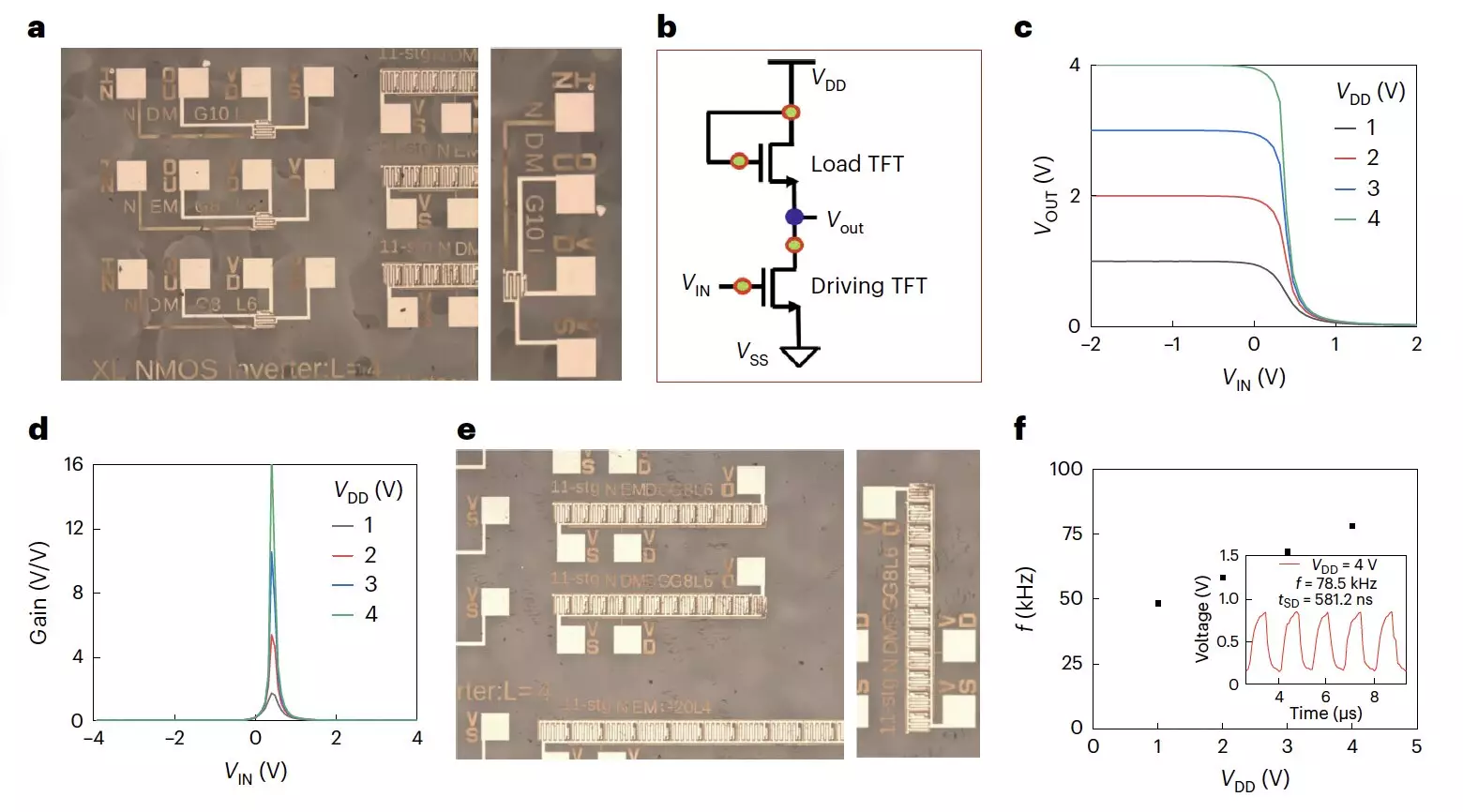
Initial tests of the n-type transistors demonstrated promising results, including high electron mobilities, minimal hysteresis, and operational stability under various bias stresses. The researchers were also able to utilize these transistors to create electronic components like all-perovskite unipolar inverters and ring oscillators, showcasing the versatility of this technology.
Moving forward, the proposed fabrication strategy for metal halide perovskite transistors holds the potential to revolutionize integrated circuit design, offering high performance at a lower cost. The integration of n-type transistors into existing electronic devices could pave the way for new and innovative applications in the field of optoelectronics.
The development of metal halide perovskite-based transistors, particularly in the realm of n-type devices, represents a significant advancement in the field of semiconductor technology. With further research and refinement, these unique materials have the potential to reshape the landscape of electronic device manufacturing, opening up a world of possibilities for efficient and cost-effective integrated circuits.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.