Wireless internet has become an integral part of daily life for people all around the world. From work to entertainment, the demand for wireless internet access continues to rise, leading to increased power consumption and carbon emissions. In order to keep up with the demands of modern applications and services while reducing energy consumption, researchers have been exploring new energy-efficient techniques for wireless communication.
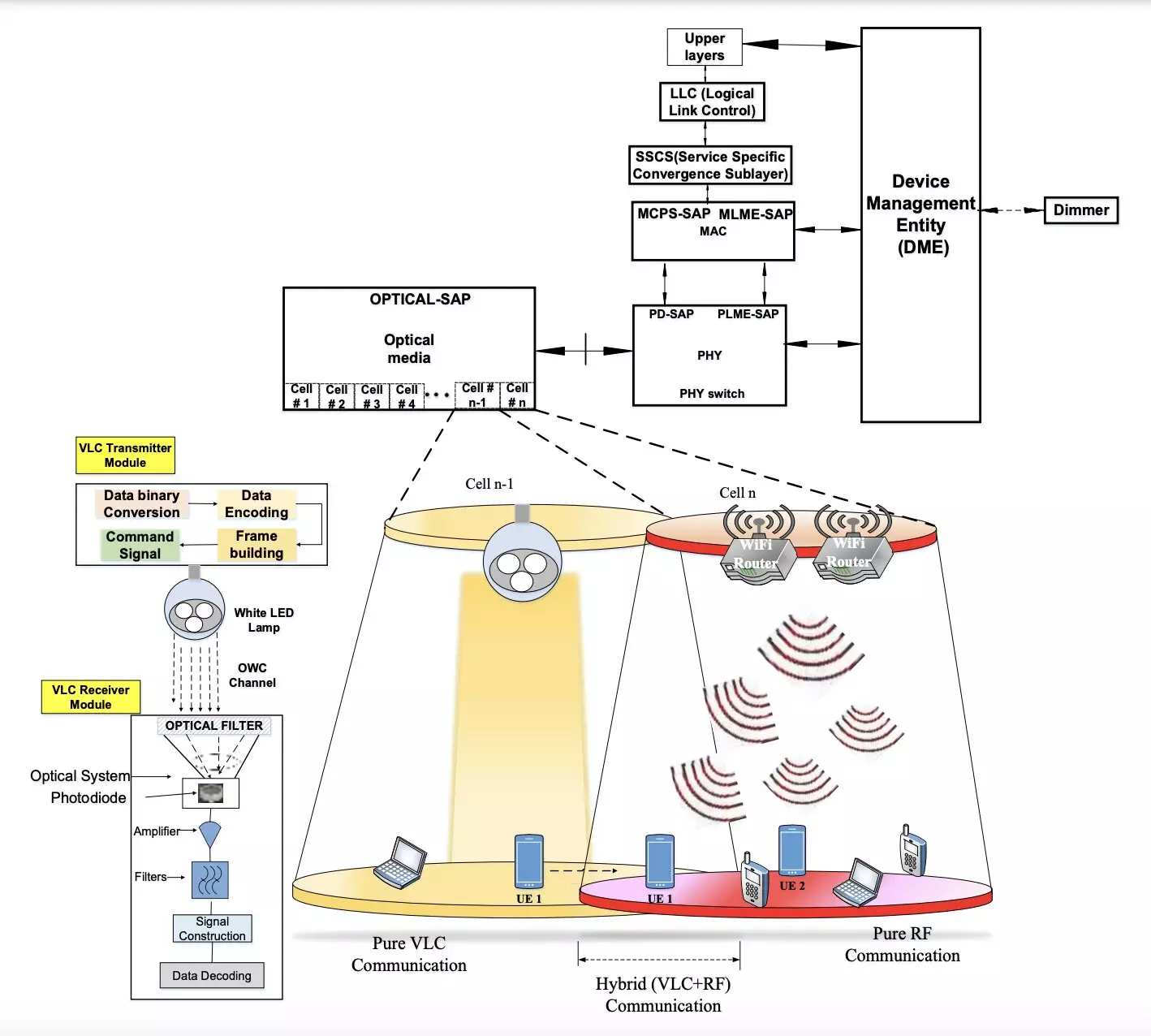
One such solution that has been gaining attention is Visible Light Communication (VLC). This method utilizes visible light to transmit data, using light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or other artificial light sources. Researchers at Central University (CU), IIDM, and CU J&K in India have recently developed a new hybrid approach that merges VLC with RF communication. This innovative solution aims to provide reliable communication in indoor environments at a high data transmission rate while consuming less energy.
The wireless communication system devised by the team of researchers consists of a transmitter and a receiver module. These two modules are physically separate but are connected via a VLC channel. The transmitter transmits binary data in the form of LED-produced light, while the receiver, which is equipped with a photosensitive device like a photodiode or a camera, extracts the information from the emitted light. The use of modulation schemes helps to maintain a continuous stream of data while keeping power consumption at a constant value.
The researchers conducted an evaluation of their proposed indoor wireless communication system using various simulation platforms. The results indicated that the system could enable stable communication between devices in the same indoor environment with significant energy savings. The hybrid system of RF and VLC showed high energy efficiency, low Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), lower incident and absorbed power density, as well as an increase in the battery lifetime of mobile devices.
The study by the team of researchers sheds light on the potential of reducing power consumption and electromagnetic radiation in wireless communication. The proposed hybrid approach offers a sustainable solution for indoor communication, maintaining the required Quality of Service and Quality of Experience for users. Further research and improvements on this approach could lead to more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly wireless communication systems in the future.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.