The Atlantic Meridional Ocean Current (AMOC) plays a crucial role in maintaining the relatively warm climate of Northern Europe. However, recent studies have shown that this important ocean current is under threat due to the effects of global warming. Scientists have long projected that the AMOC could cease to function by the year 2200, but new observations suggest that this timeline might be accelerated.
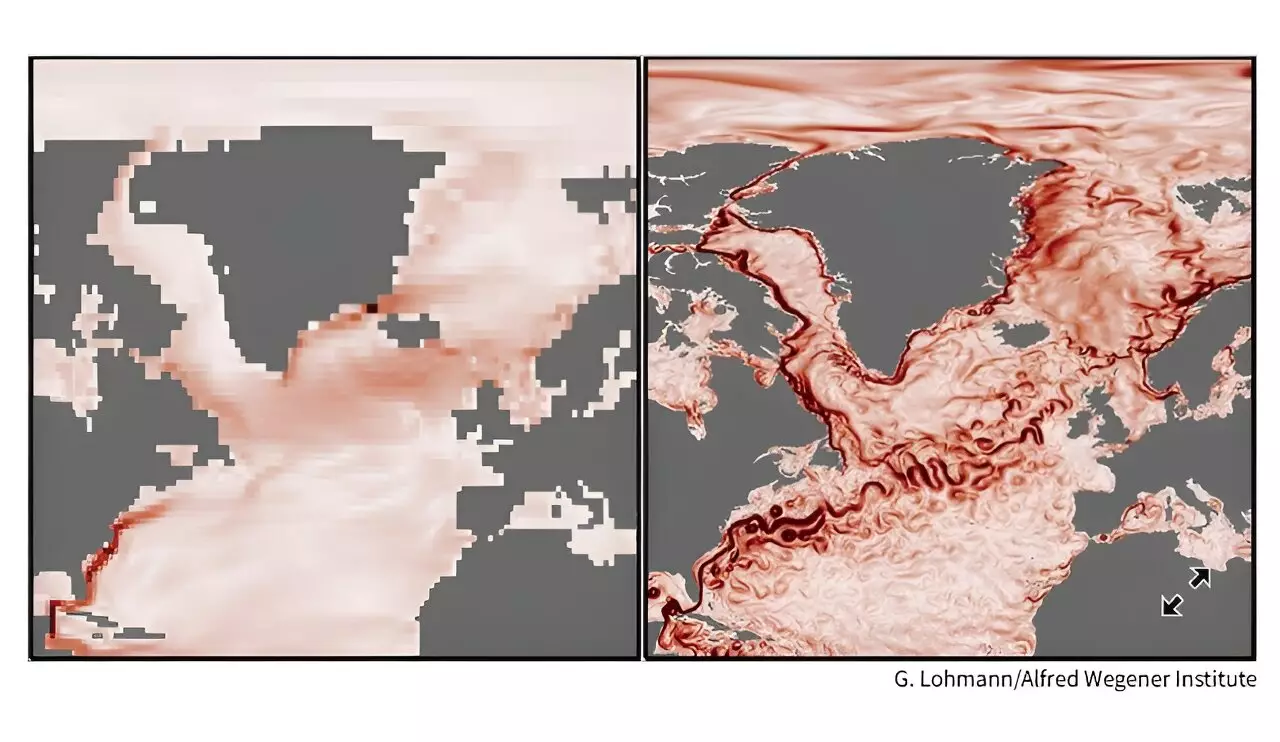
While previous climate models have provided some insight into the behavior of the AMOC, a new high-resolution climate model has offered a more detailed understanding of this complex system. By using the Community Earth System Model with a grid size of 0.1°, researchers were able to uncover previously unknown features of the AMOC. This new model revealed that the AMOC may undergo abrupt collapses in some regions while unexpectedly strengthening in others.
The study also examined the impact of greenhouse gas emissions on the AMOC. Under the IPCC’s RCP 8.5 scenario, where carbon dioxide levels are projected to rise rapidly, the AMOC showed an overall slowdown by about 8 million cubic meters of water per second from 2000 to 2100. This drastic decline is expected to occur around the year 2020, with potential long-term consequences for the climate system.
Regional Variations and Tipping Points
One of the key findings of the study was the presence of tipping points within the AMOC system. These tipping points represent thresholds at which small changes can lead to sudden shifts in the behavior of the AMOC. While previous models had not accounted for these tipping points, the high-resolution model revealed their existence. This highlights the need to incorporate regional dynamics into future AMOC forecasts to better understand the potential impacts on climate and marine ecosystems.
As the effects of global warming continue to unfold, it is crucial to advance climate models to anticipate and respond to the changes in the Earth’s systems. The feedback between the overall AMOC and smaller-scale variations could play a significant role in shaping the future climate of Northern Europe and beyond. By gaining a more nuanced understanding of the AMOC, scientists can better prepare for the potential scenarios that lie ahead.
The future of the Atlantic Meridional Ocean Current is uncertain, but with the use of advanced climate models and ongoing research, scientists are working to unravel the complexities of this vital ocean current. By incorporating regional dynamics and tipping points into their forecasts, researchers hope to gain a more comprehensive understanding of how the AMOC will evolve in a changing climate.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.